Tag Archives: winforms
Create shortcut programmatically in C#
In cases where we need to create a shortcut for our application or for any other reason, the Windows Script Host Object Model library allows us to do just that.
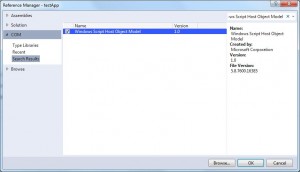
In order to access the classes that will enable us to create shortcuts we need to add the Windows Script Host Object Model library as a reference to our project first.
- Right click on your project
- Click “Add Reference…”
- Select the “COM” tab on the left
- Search for Windows Script Host Object Model and add it as a reference
After you successfully add the reference in your project you should be able to use the snippet bellow to create shortcuts as you please.
Create shortcut:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public static void CreateShortcut(string shortcutName, string shortcutPath, string targetFileLocation) { string shortcutLocation = System.IO.Path.Combine(shortcutPath, shortcutName + ".lnk"); WshShell shell = new WshShell(); IWshShortcut shortcut = (IWshShortcut)shell.CreateShortcut(shortcutLocation); shortcut.Description = "My shortcut description"; // The description of the shortcut shortcut.IconLocation = @"c:\myicon.ico"; // The icon of the shortcut shortcut.TargetPath = targetFileLocation; // The path of the file that will launch when the shortcut is run shortcut.Save(); // Save the shortcut } |
Usage:
1 | CreateShortcut("my shortcut", Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop), Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location); |
Start application at Windows startup with C#
The following snippet will allow you to add your application in the registry so it will launch when Windows start. Alternative you can use Environment.SpecialFolder.Startup to place a shortcut of your application in the startup folder which will have the same effect.
Note that this snippet will add an entry in HKEY_CURRENT_USER which means the program will only launch at startup for the user that is currently logged in when you run the code. If you want your program to run at startup for all users you will need to use HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE instead but keep in mind that you will require administration rights in order to do that.
Register program to start with Windows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public static void AddApplicationToStartup() { using (RegistryKey key = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey("SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run", true)) { key.SetValue("My Program", "\"" + Application.ExecutablePath + "\""); } } |
Stop program from starting with Windows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public static void RemoveApplicationFromStartup() { using (RegistryKey key = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey("SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run", true)) { key.DeleteValue("My Program", false); } } |
How to allow only one application instance
The following code will ensure that your application can only have one instance active. If the user tries to open the application again while the application is already running then the application will simply quit (in this case after showing a message).
For this to work we will need to modify the Program.cs to check with the use of Mutex if the application is already running or not before we open the main form. Our check will take place in the Main method.
Your code in Program.cs should look like this:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | using System; using System.Reflection; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; using System.Threading; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace WindowsFormsApplication1 { static class Program { [STAThread] static void Main() { /* Retrieve the application Guid attribute. Alternative you can simply use the application name to initialize the Mutex * but it might be risky as other programs might have similar name and make use of the Mutex class as well. */ GuidAttribute appGuid = (GuidAttribute)Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetCustomAttributes(typeof(GuidAttribute), true)[0]; // The boolean that will store the value if Mutex was successfully created which will mean that our application is not already running. bool createdNew = true; // Initialize the Mutex object. using (Mutex mutex = new Mutex(true, appGuid.Value, out createdNew)) { /* If Mutex was created successfully which means our application is not running run the application as usual * or else display a message and close the application.*/ if (createdNew) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false); Application.Run(new Form1()); } else { MessageBox.Show("Application is already running"); } } } } } |
Feel free to modify the example to suit your needs.
Get value between two strings
You might find this snippet particular useful in cases where you want to get a value between two other values.
This takes advantage of the string’s Split overload to pass an array of two values. This will result in the string being split twice, once for the first value in the array and once more for the second value. The result will be that the second value in the array that Split returns is the actual value between the first and the second value we passed as argument.
Code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | private string GetBetween(string strSource, string strStart, string strEnd) { string result = string.Empty; if (strSource.Contains(strStart) && strSource.Contains(strEnd)) { result = strSource.Split(new string[] { strStart, strEnd }, StringSplitOptions.None)[1]; } return result; } |
Example:
1 2 3 4 | string source = "this is (my value) a test"; // Returns "(my value)" GetBetween(source, "this is ", " a test"); |