Check if user has administartor rights
In numerous cases it is essential to know if the user has administrator rights or not. A good example for this would be when we want to decide if we want to write a value in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE which requires administrator rights or HKEY_CURRENT_USER which doesn’t.
The following method will return true if the application is running under administration rights or false if its not.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | public static bool IsUserAdministrator() { WindowsIdentity user = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent(); WindowsPrincipal principal = new WindowsPrincipal(user); return principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator); } |
Create shortcut programmatically in C#
In cases where we need to create a shortcut for our application or for any other reason, the Windows Script Host Object Model library allows us to do just that.
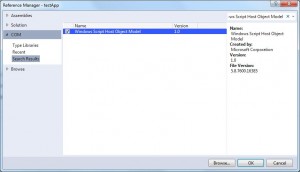
In order to access the classes that will enable us to create shortcuts we need to add the Windows Script Host Object Model library as a reference to our project first.
- Right click on your project
- Click “Add Reference…”
- Select the “COM” tab on the left
- Search for Windows Script Host Object Model and add it as a reference
After you successfully add the reference in your project you should be able to use the snippet bellow to create shortcuts as you please.
Create shortcut:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | public static void CreateShortcut(string shortcutName, string shortcutPath, string targetFileLocation) { string shortcutLocation = System.IO.Path.Combine(shortcutPath, shortcutName + ".lnk"); WshShell shell = new WshShell(); IWshShortcut shortcut = (IWshShortcut)shell.CreateShortcut(shortcutLocation); shortcut.Description = "My shortcut description"; // The description of the shortcut shortcut.IconLocation = @"c:\myicon.ico"; // The icon of the shortcut shortcut.TargetPath = targetFileLocation; // The path of the file that will launch when the shortcut is run shortcut.Save(); // Save the shortcut } |
Usage:
1 | CreateShortcut("my shortcut", Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop), Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().Location); |
Start application at Windows startup with C#
The following snippet will allow you to add your application in the registry so it will launch when Windows start. Alternative you can use Environment.SpecialFolder.Startup to place a shortcut of your application in the startup folder which will have the same effect.
Note that this snippet will add an entry in HKEY_CURRENT_USER which means the program will only launch at startup for the user that is currently logged in when you run the code. If you want your program to run at startup for all users you will need to use HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE instead but keep in mind that you will require administration rights in order to do that.
Register program to start with Windows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public static void AddApplicationToStartup() { using (RegistryKey key = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey("SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run", true)) { key.SetValue("My Program", "\"" + Application.ExecutablePath + "\""); } } |
Stop program from starting with Windows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | public static void RemoveApplicationFromStartup() { using (RegistryKey key = Registry.CurrentUser.OpenSubKey("SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run", true)) { key.DeleteValue("My Program", false); } } |
Visual Studio 2012 Update 3
Microsoft released Visual Studio 2012 Update 3 (Visual Studio 2012.3) on June 26, 2013. This update introduces TFS build improvements as well as various bug fixes.
You can download the update from Microsoft’s download centre using the links below. Alternative you can use the links bellow to download the installation file that better suits your needs.
Note: Visual Studio 2012 Update 4 is now available. You can download it for free using the download links below.
Download Links
Web installation file: http://go.microsoft.com/?linkid=9821199
Offline installation file: http://go.microsoft.com/?linkid=9833082
Posted in Microsoft, Software Updates.
Tagged Microsoft, Visual Studio, Visual Studio 2012